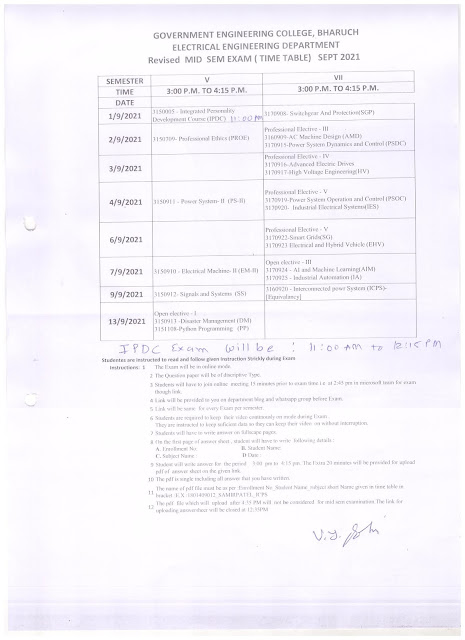
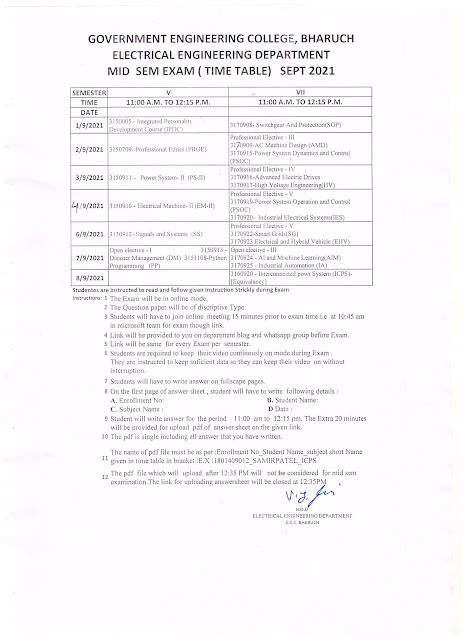
Tuesday 31 August 2021
Important Notice for 5th semester
Tomorrow exam time for subject IPDC will be 11:00 am to 12:15 pm. All are informed to join link at 10:45 am.
This is for tomorrow only.
Sunday 29 August 2021
MID SEM Syllabus for the Subject Industrial Automation (7th sem Open Elective Subject)
MID SEM Syllabus (7th Sem, Electrical Open Elective Subject)
Industrial Automation
Subject Code: 3170925 , Semester – VII
Introduction:
Automation overview, Requirement of automation systems, Architecture of
Industrial Automation system, Introduction of PLC and supervisory control and
data acquisition (SCADA). Industrial bus systems: modbus & profibus. Role
of computers in measurement and control.
Automation
components: Sensors for temperature, pressure, force, displacement, speed,
flow, level, humidity and pH measurement. Actuators, process control valves,
power electronics devices DIAC, TRIAC, power MOSFET and IGBT. Introduction of
DC and AC servo drives for motion control.
Programmable logic
controllers: Programmable controllers, Programmable logic controllers,
Analog digital input and output modules, PLC programming, Ladder diagram, PLC Communication and networking, PLC
selection, PLC Installation, Advantage of using PLC for Industrial automation,
Application of PLC to process control industries.
Friday 27 August 2021
List of Nonregistered Students in Design Engineering I A 3rd Sem
Question Banks for SMTG (3170922) (7TH SEM) 2021
Thursday 26 August 2021
Question Bank Of The COurse_ Professional Ethics (3150709)
Wednesday 25 August 2021
Tuesday 24 August 2021
Power System-II(3150911) Mid semester Examination Syllabus-september-2021
Monday 23 August 2021
MID SEM_SYLLABUS_Electrical and Hybrid Vehicle_3170923_7th SEM_ODD SEM_2021-22
Semester
– VII Subject
Name: Electrical and Hybrid Vehicle
Subject Code: 3170923
MID SEMESTER EXAM SYLLABUS
1. Introduction to Electric Vehicle:
History of Electric Vehicles, Development towards 21st Century, Types of Electric Vehicles in use today – Battery Electric Vehicle, Hybrid (ICE & others), Fuel Cell EV, Solar Powered Vehicles. Motion and Dynamic Equations of the Electric Vehicles: various forces acting on the Vehicle in static and dynamic conditions.
2. Induction to Hybrid Electric Vehicle:
Social and environmental importance of hybrid and electric vehicles, impact of modern drive-trains on energy supplies. Hybrid Electric Drive-trains: Basic concept of hybrid traction, introduction to various hybrid Drive-train topologies, power flow control in hybrid drive-train topologies, fuel efficiency analysis.
3.Electric Drive Trains:
Basic concept of electric traction, introduction to various electric drive- train topologies, power flow control in electric drive-train topologies, fuel efficiency analysis. Electric Propulsion unit: Introduction to electric components used in hybrid and electric vehicles, Configuration and control of DC Motor drives, Configuration and control of Induction Motor drives, configuration and control of Permanent Magnet Motor drives, Configuration and control of Switch Reluctance Motor drives, drive system efficiency.
4. Introduction to Energy Storage Requirements in Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Battery based energy storage and its analysis, Fuel Cell based energy storage and its analysis, Super Capacitor based energy storage and its analysis, Flywheel based energy storage and its analysis, Hybridization of different energy storage devices. Sizing the drive system: Matching the electric machine and the internal combustion engine (ICE)
Course Outcomes:
After completing the course, students will be able to;
Sr. No. | CO statement |
CO-1 | Select appropriate source of energy for the hybrid electric vehicle based on driving cycle. |
CO-2 | Analyze the power and energy need of the various hybrid electric vehicle. |
CO-3 | Measure and Estimate the energy consumption of the Hybrid Vehicles. |
CO-4 | Evaluate energy efficiency of the vehicle for its drive trains. |
MID SEM_SYLLABUS_SMART GRID_3170922_7th SEM_ODD SEM_2021-22
Semester – VII Subject
Name: Smart grids
Subject Code: 3170922
MID
SEMESTER EXAM SYLLABUS
|
Chapter No. |
Content |
|
1 |
Basics of Load and Generation, Grid operation, Concepts of Power Flow Analysis, Economic Dispatch and Unit Commitment. Introduction to Smart Grid, Difference between conventional & smart grid, Architecture of Smart Grid, Smart Grid standards, Policies Applications, Smart Grid control layer and elements, Smart Grid Initiative for Power Distribution Utility in India. |
|
3 |
Distributed generation resources, Advantages and disadvantages of DG, Distributed Generation Utilization Barriers, Distributed Generation integration to power grid Smart Grid components control elements, Smart Grid Technologies |
|
4 |
Micro Grids, Concept of micro grid, need & applications of micro grid, formation of micro grid, Modelling of AC Smart Grid components, Modelling of DC Smart Grid components, Modelling of storage devices, issues of interconnection, Operation, protection & control of micro grid. Simulation and case study of AC micro grid Islanding, need and benefits, different methods of islanding detection. |
|
5 |
Load dispatch centers, Sensor Networks, Phasor Measurement Units, Communications Infrastructure, Fault Detection and Self-Healing Systems, Applications and Challenges, , wide-area monitoring system (WAMS), Phasormeasurement units PMU; Smart sensors/telemetry, advanced metering infrastructure(AMI);smart metering; smart grid system monitoring, |
Course Outcomes:
After completing the course, students will be able to;
|
Sr. No. |
CO statement |
|
CO-1 |
Summaries various aspects of the smart grid Technologies, Components,Architectures and Applications |
|
CO-2 |
Study and compare modern communication infrastructure and justify the feasibility of the same for smart grid applications. |
|
CO-3 |
Analyze Micro grid and distributed generation as a part of modern hybrid powersystem with advantages and challenges in smart gird operations |
|
CO-4 |
Use of load modeling techniques, Demand Side Ancillary Services EnergyManagement in Pricing and Energy Consumption Scheduling in smart gridoperations |
Syllabus of MID_Exam_Sept_2021_Power system Operation And control_2170919
1. Automatic Generation Control and Voltage Control: Introduction;
Load Frequency Control (Single Area Case); Load Frequency Control and Economic Despatch Control; Two-Area Load Frequency Control; Optimal (Two-Area) Load Frequency Control; Automatic Voltage Control; Load Frequency Control with Generation Rate Constraints (GRCs); 8
2. Reactive Power and Voltage Control: Introduction;
Reactive power requirement of an uncompensated line; Implication of surge impedance loading; Reactive loss characteristics of transmission line; Operation of a transmission line at no load condition; Operation of a transmission line under heavy loading condition; Voltage regulation of the transmission line and its relation with reactive power; Maximum power transfer in an uncompensated line; Line loadability. Reactive powervoltage (Q-V) coupling concept; Operational aspects in reactive power and voltage control; Basic principle of system voltage control; Reactive power flow constraints and their implications in loss of voltage; Power System Voltage Stability : Introduction, Difference between angle stability and voltage stability, Causes of voltage instability, types, proximity and mechanism of voltage stability, Practical aspects of reactive power flow problems leading to voltage collapse in EHV lines. 10
3. Power System Security: Introduction;
System State Classification; Security Analysis; Contingency Analysis; Sensitivity Factors: generation shift distribution factor, line shift distribution factor
4.Load Forecasting: Introduction;
Forecasting Methodology; Estimation of Average and Trend Terms; Estimation of Periodic Components; Estimation of ys(k): Time Series Approach; Estimation of Stochastic Component: Kalman Filtering Approach; Long-Term Load Predictions Using Econometric Models; Reactive Load Forecasting.
Course Outcome
CO-1 Apply concepts of frequency control and voltage control in small sample single area power system
CO-2 Analyze performance of transmission lines with respect to reactive power requirement for voltage stability
CO-4 Describe concepts of power system security and load forecasting
Mid Sem Exam Syllabus for Odd Sem AY 2021-22_7 TH SEM_PEC IV_3170917 – HVE
Electrostatic fields and field stress control:
Electrical field distribution and breakdown strength of insulating materials - fields in homogeneous, isotropic materials - fields in multi-dielectric, isotropic materials.
Numerical analysis of electrical fields in high voltage equipment:
numerical methods - Charge simulation method (CSM), Finite Difference Method (FDM), Finite Element Method (FEM), The boundary-element method, Comparative summary, Formulation of the finite-element equations in two and three dimensions - Forming the functional equation, The energy functional illustrated, Numerical representation.
Electrical breakdown in gases:
Gases as insulating media - ionization and decay processes, Townsend first ionization coefficient, photo ionization, ionization by interaction of metastable with atoms, thermal ionization, deionization by recombination, deionization by attachment–negative ion formation, examples - cathode processes – secondary effects, photoelectric emission, electron emission by positive ion and excited atom impact, thermionic emission, field emission, Townsend second ionization coefficient, secondary electron emission by photon impact, examples - transition from non-self-sustained discharges to breakdown, the Townsend mechanism, examples - the streamer or ‘kanal’ mechanism of spark, examples - the sparking voltage– Paschen’s law, penning effect.
Breakdown in liquid :
Liquid as insulators, breakdown in liquids - electronic breakdown, suspended solid particle mechanism, cavity breakdown, examples - static electrification in power transformers, transformer oil filtration, transformer oil test, alternative liquid insulations like vegetable oils, esters and silicon oils.
Generation of high voltages:
Generation of high direct voltages, half and full wave rectifier circuits, voltage multiplier circuits, Van de Graff generators, electrostatic generators, examples - generation of alternating voltages, testing transformers, cascaded transformers, resonant transformers, examples - impulse voltages, Standard lightning and switching surge and associated parameters and their corrections, design and construction of impulse voltage generator circuits, Marx circuit, operation, examples - impulse current generator.
Measurement of high voltages:
High direct voltage measurement, peak voltage measurements by spark gaps, sphere gaps, reference measuring systems, uniform field gaps, rod gaps, factors affecting sphere gap measurements, examples - electrostatic voltmeters - ammeter in series with high ohmic resistors and high ohmic resistor voltage dividers.
High voltage testing:
Testing of insulators and bushings, testing of isolators and circuit breakers Testing of cables, testing of transformers - testing of surge diverters.
Course Outcome:
1. Apply numerical methods for engineering problem. (Applying) -20%
2. Recall breakdown mechanism for dielectric materials in solid, liquid and gaseous state. (Remembering) -20%
3. Classify insulation test techniques. (Understanding) -20%
4. Examine methods for generation of test high voltage and as well for its measurement. (Analyzing).-20%
Syllabus_Professional Ethics_3150709_MID_EXAM_SEPT_2021
1 Concepts and theories of Business Ethics:
Definitions of Ethics, Personal ethics and Business ethics, Morality and law, How are moral standards formed? Religion and Morality, Morality, Etiquette and Professional codes, Indian Ethical Traditions.
2 Business Ethics: Principles of personal Ethics,
Principles of Professional ethics, Evolution of Ethics Over the years, Honesty, Integrity and Transparency are the touchstones of Business Ethics, Distinction Between Values and Ethics, Roots of Unethical Behaviour, Ethical Decision–Making
3 Ethical Dilemmas,
Sources and Their resolutions: What is an Ethical Dilemma, Sources of Ethical Behaviour, Code of Personal Ethics for Employees, How to Resolve an Ethical Problem, How to Resolve Ethical Dilemmas.
4 Ethical Decision – marking in Business:
Ethical Models that Guide Decision making, Which Approach to use, Ethical Decision Marking with Cross – holder conflicts and competition, Applying Moral Philosophy to Ethical Decision Making, Kohlberg’s Model of Cognitive Moral Development, Influences on Ethical Decision Making, Personal values and Ethical Decision Marking
CO-1
Awareness of types of ethical challenges and dilemmas confronting members of a range of professions (business, media, police, law, medicine, research) 25 % MARKS
CO-2
Identify and describe relevant theoretical concepts related to professional ethics in engineering 20% MARKS
CO-3
Understand the basic perception of profession, professional ethics, various moral issues & uses of ethical theories 20 % MARKS
CO-4
Distinguish among morals, values, ethics, and the law and to explore how they each impact engineering practice 25% MARKS
All COs are compulsory means all Chapters are compulsory and per chapter One Question.
3170915 – PSDC - Mid – Sem Exam Syllabus for Odd Sem AY 2021-22
Syllabus: Click Here
Saturday 21 August 2021
|
MID-SEMESTER TEST ,
SYLLABUS for A C Machine Design(3170909)(7Th Semester- Electrical) |
(1)Introduction
Major considerations in electrical machine design, Electrical engineering materials, Spacefactor, Choice of specific electrical and magnetic loadings, Thermal considerations, Heatflow, Temperature rise, Rating of machines.
(2) Design of transformers
Sizing of a transformer, Main dimensions, kVA output for single- and three-phase transformers, Window space factor, Overall dimensions, Operating characteristics,voltage regulation
(3)
Design of induction motors
Sizing of an induction motor, Main dimensions, Length of air gap, Rules for selecting rotorslots of squirrel cage machines, Design of rotor bars & slots, Design of end rings, Design of wound rotor, Magnetic leakage calculations, Leakage reactance of poly phase machines, Magnetizing current, Short circuit current,
(4)
Design of synchronous machines
Sizing of a synchronous machine, Main dimensions, Design of salient pole machines, Short circuit ratio and its significance, Shape of pole face, Armature design, Armature parameters, Estimation of air gap length, Design of rotor, Design of damper winding,
MID-SEMESTER TEST, SYLLABUS Industrial Electrical Systems (3170920)(7Th Semester- Electrical)
MID-SEMESTER TEST, SYLLABUS for
Industrial Electrical Systems (3170920)(7Th Semester- Electrical)
(1) Electrical System Components
LT system wiring components, selection of cables, wires, switches, distribution box,metering system, Tariff structure, Protection components- Fuse, MCB, MCCB, ELCB, Symbols for wiring components, Single line diagram (SLD) of awiring system, Contactor, Isolator, Relays, MPCB, Electric shock and Electrical safety practices
(2Residential
and Commercial Electrical Systems
Types of residential and commercial wiring systems, General rules and guidelines for installation, Load calculation and sizing of wire, Rating of main switch, distribution board and protection devices, Earthing system calculations, Requirements of commercial installation, Deciding lighting scheme and number of lamps, Earthing of commercial installation, Selection and sizing of components
(3)
Illumination Systems
Understanding various terms regarding light- lumen, intensity, candle power, lamp efficiency, specific consumption, glare, space to height ratio, waste light factor, depreciation factor, Various illumination schemes, Incandescent lamps and modern luminaries like CFL, LED and their operation, Energy saving in illumination systems, Design of a lighting scheme for a residential and commercial premises, Flood lighting
(4) Industrial Electrical Systems
DG Systems, UPS System, Electrical Systems for the elevators, Battery banks,Sizing the DG, UPS and Battery Banks, Selection of UPS and Battery Banks
(5) Industrial Electrical System Automation
Study of basic PLC, Role of automation, Advantages of process automation,
Wednesday 18 August 2021
Sunday 15 August 2021
Link to veryfy 6th sem MID mark(Summer-2021) on GTU Portal
Dear students,
You can view your 6thsem mid marks on GTU portal for the three days 15,16 and 17 August.
So you are informed to view your subject-wise marks and fill below link. Fill this link up to 17th August 5:00.PM.
https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSfY5rUOz6plcTCTFIrLOhugtG52SBDxnAsVYSZK9sKHYXtgdw/viewform